File: <hippoboscidaemed.htm> <Medical
Index> <General Index> Site Description
Glossary <Navigate to Home>
|
HIPPOBOSCIDAE (Contact) Please
CLICK on
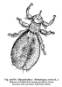
underlined links to view: Hippobosidae. -- The louse
flies and sheep ked
eggs and larvae develop within the mother fly and are nourished from
glands. The "nits" pupate
immediately upon being released. The
adults are either winged or wingless.
The winged species are dark brown and about the size of small
houseflies and are common on birds.
The sheep ked, Melophagus ovinus
(L.) is wingless and parasitic on sheep. Control of
these flies is relatively simple.
Subjecting animals to various sprays, dips and dusts in autumn is
usually adequate. Also by removing
sheep from old pens and spraying the pen area with insecticides eliminates
the flies. = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = Key References: <medvet.ref.htm> <Hexapoda> [Additional references may be found at: MELVYL Library] Dick,
C. W. 2006. Checklist of World Hippoboscidae (Diptera:
Hippoboscoidea). Chicago Dept.Zool.,
Field Mus. Nat. Hist. Hutson, A.M. 1984. Diptera: Keds,
flat-flies & bat-flies (Hippoboscidae & Nycteribiidae). Handbks.
Ident. British Insects 10 pt 7. Roy.
Ent. Soc. London. p. 84. Jackson
S. W. & W. Nixon. 1992. Incidence
of louse-flies (Hippoboscidae) in some Alaskan birds. North American Bird Bander. 17 (2): 65–8 Matheson, R. 1950. Medical Entomology. Comstock Publ. Co, Inc. 610 p. Service, M. 2008.
Medical Entomology For Students. Cambridge Univ. Press. 289 p Legner, E.
F.
1995. Biological
control of Diptera of medical and veterinary importance. J. Vector Ecology 20(1): 59-120. Legner, E. F.. 2000.
Biological control of aquatic Diptera. p. 847-870.
Contributions to a Manual of Palaearctic Diptera, Vol. 1, Science Herald, Budapest. 978 p. Maa, T. C. 1969. a Revised
Checklist & Concise Host Index of Hippoboscidae (Diptera). Pacific Insects Monog., Honolulu: Bishop
Museum, Honolulu, Hawaii.
20: 261–299.
Petersen, F. T. & R. K. Meier, et.
al. 2007. The phylogeny and evolution of host choice
in the Hippoboscoidea (Diptera) as reconstructed using
four molecular markers.". Mol. Phylogenetics &Evolution. 45
(1): 111–122. |
FURTHER DETAIL = <Entomology>, <Insect Morphology>, <Identification Keys>
.