File: <thysanoptera.htm> : < (Entomology), (Invertebrates), (General
Index)> <Invertebrate Bibliography> <Glossary> <Site Description>
< Home>
|
Entomology: THYSANOPTERA 1 Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Hexapoda: Class: Insecta: Order: Thysanoptera (Contact)
Please CLICK on underlined
categories to view and on included illustrations to enlarge: Depress Ctrl/F to search for subject matter:
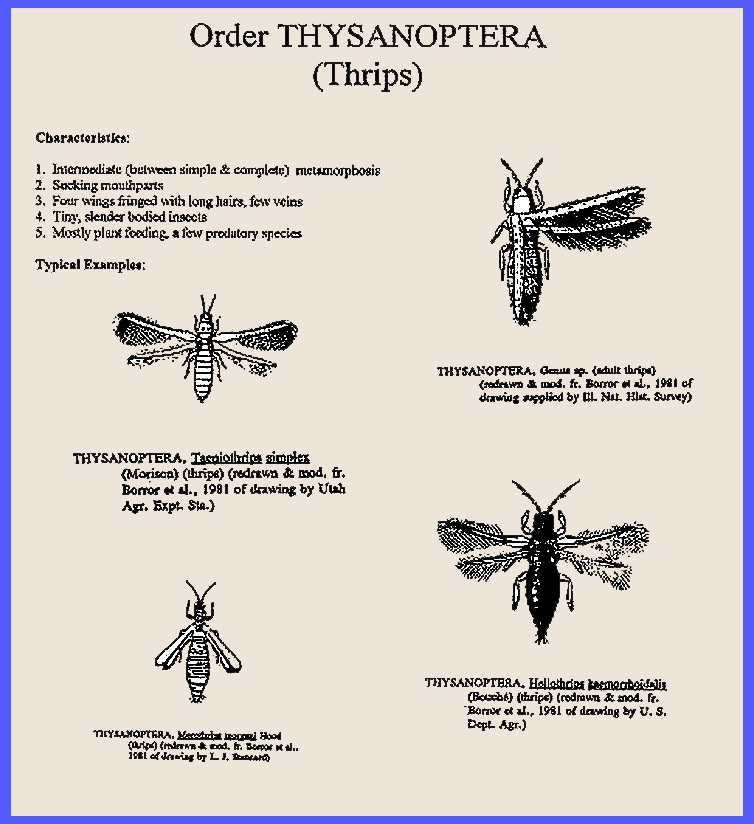
General Summary of
Thysanoptera The Thysanoptera -- <Adults>
& <Juveniles> -- are tiny insects, 0.5 to
12 millimeters, with asymmetrical piercing rasping-sucking mouthparts and a
short labial proboscis. Their
prothorax is large and free. The
tarsus has two or three joints with a terminal extendable vesicle. Both winged and wingless forms occur. When present there are two pairs of
similar wings, provided with a fringe of prominent long hairs, which appear
as feathers, and few veins if at all are present. Metamorphosis is more complex than
most insects and it includes an incipient pupal instar. Instar 1 and 2 are simple with no wing
pads. Instar 3 has wing pads. The 4th instar is quiescent and changing
enclosed in a cocoon. . Parthenogenesis is of common. In
the pea thrips, Kakothrips robustus, the eggs are inserted in the stamen
sheath of the flower and the nymphs emerging feed on the young fruit,
inhibiting its growth. Later they feed on the soft tissues of pea pods,
causing scar-like markings. The nymphs leave the plant and bury themselves
deeply in the ground, where they remain until the following spring, when they
pupate. Common thrips in Europe are Taeniothrips inconsequens of pears
and Anaphothrips striatus of grasses and cereals (Borradaile
& Potts, 1958). Their direct feeding activity gives
plant leaves a silvery appearance.
They are able to transmit the Spotted-wilt virus to
tomatoes. The citrus thrips and
gladiola thrips are very destructive, the latter damaging the corms in
storage. The bean thrips feed on the leaves
of cotton and beans. They are also
very important pests of pears where they attack the flower buds and prevent
their development. The onion thrips attacks a wide
range of plants. It causes a
distortion to the foliage of onion and is especially serious on onion seed
crops. It fees mostly on the leaf
sheath, but will also attack the blossoms.
The males are wingless, but females have wings and they reproduce
parthenogenetically. The gestation
period is only 20 days. ---------------------------------- Thysanoptera --Biological Control Projects (1%
of total projects) Cuban Laurel Thrips, Gynaikothrips ficorum Marchal <ch-36.htm> ------------------------------------------- Details
of Insect Taxonomic Groups Examples of beneficial species
occur in almost every insect order, and considerable information on
morphology and habits has been assembled.
Therefore, the principal groups of insect parasitoids and predators
provide details that refer to the entire class Insecta. These details are available at <taxnames.htm>. ============== |